
The Council of Baltic Sea States (CBSS) is an intergovernmental forum created among the countries of the basin with the aim to foster their co-operation in a number of fields, from economics to environment, transport to education.
Member states
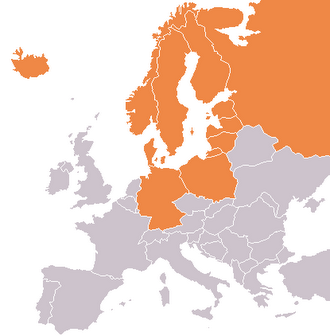
The CBSS has 12 member states, namely:
  Denmark      Germany    Norway      SwedenÂ
  Finland        Estonia      Iceland     Latvia
  Lithuania      Poland       Russia       European Commission
 Â
History
As a response to the pressures for continental reunification emerging in Europe after the Cold War, in March 1992, in Copenhagen, Denmark, Germany, Norway, Finland, Sweden, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia and Iceland agreed to create the Council of Baltic Sea States (CBSS) with the participation of the European Commission. Environmental protection, energy, trade, culture and the protection of human rights have been the key objectives on which the Council of Baltic Sea States has based its Action Strategy. At an economic level, customs procedures have been simplified contributing to the growth of trade. At the same time, cross-border co-operation has been strengthened on projects concerning communications.
Focusing on subjects related to regional and international politics, the intergovernmental forum has been able to increase the visibility of the Baltic quadrant in the wider European context. However, for Brussels the Council, which brings together members from both inside and outside the EU, is a strategic platform for political debate.
The Conference of foreign ministers
The Conference is the highest-level body of CBSS. It meets every two years and is responsible for defining the guidelines of the dialogue process. Â Â
The Ministerial Committee of Senior Officials (CSO)
The Committee, costituted of leading representatives of the Ministries of Foreign Affairs, has the function to assist the Council Presidency and to coordinate the organisationâs activities.
The Expert Groups
The Expert Groups are in charge of carrying out sectorally the Council's initiatives and programs. There are five expert groups, namely:
- The Expert Group on Economic Co-operation (WGEC),
- The Expert Group on Nuclear and Radiation Safety (WGNRS),
- The Expert Group on Youth Issues,
- The Expert Group on Customs Co-operation and Border-Crossing Aspects (WGCCBA),
- The Expert Group on Maritime Policy.Â
The Permanent International Secretariat
Created In 1998, in Stockholm, the Permanent Secretariat has the function to provide technical support to the decision-making structures of the Council, ensuring enhanced coordination of organization's initiatives. Â
RELATED VIDEO




 The Council of the Baltic Sea States (CBSS) is an overall political forum for regional intergovernmental cooperation which addresses the five priority areas of the environment, economic development, energy, education and culture, civil security and human dimension...
The Council of the Baltic Sea States (CBSS) is an overall political forum for regional intergovernmental cooperation which addresses the five priority areas of the environment, economic development, energy, education and culture, civil security and human dimension...








